Piriformis Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Piriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from compression of the sciatic nerve by the
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Early (proximal) divisions of the sciatic nerve into its tibial and common peroneal components can predispose patients to piriformis syndrome, with these branches passing through and below the piriformis muscle or above and below the muscle. *Acquired * Sitting for prolonged periods (office workers, taxi drivers, bicycle riders) * Overuse syndromes: Piriformis muscle hypertrophy (viz., in athletes) * Trauma to the hip or buttock area

 Piriformis syndrome (PS) data is often confused with other conditions due to differences in definitions, survey methods and whether or not occupational groups or general population are surveyed. This causes a lack of group harmony about the diagnosis and treatment of PS, affecting its
Piriformis syndrome (PS) data is often confused with other conditions due to differences in definitions, survey methods and whether or not occupational groups or general population are surveyed. This causes a lack of group harmony about the diagnosis and treatment of PS, affecting its
piriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.
The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inse ...
. Symptoms may include pain and numbness in the buttock
The buttocks (singular: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are compose ...
s and down the leg. Often symptoms are worsened with sitting or running.
Causes may include trauma to the gluteal muscle
The gluteal muscles, often called glutes are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus muscle, gluteus maximus, gluteus medius muscle, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscle ...
, spasms of the piriformis muscle, anatomical variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categ ...
, or an overuse injury. Few cases in athletics, however, have been described. Diagnosis is difficult as there is no definitive test. A number of physical exam maneuvers can be supportive. Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
is typically normal. Other conditions that may present similarly include a herniated disc
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical ...
.
Treatment may include avoiding activities that cause symptoms, stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling ...
, physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
, and medication such as NSAIDs. Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
or botulinum toxin injections may be used in those who do not improve. Surgery is not typically recommended. The frequency of the condition is unknown, with different groups arguing it is more or less common.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms includegluteal
The gluteal muscles, often called glutes are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. The three muscles originate from the ilium and sacr ...
pain that may radiate down buttock and the leg, and that is made worse in some sitting positions.
Etiology
Causes of piriformis syndrome include the following *Anatomic anomalies, present since birth: * Bipartite piriformis muscle * Sciatic nerve course/branching variations with respect to the piriformis muscle: In over 80% of the population, the sciatic nerve courses deep to and exits inferiorly to the piriformis muscle belly/tendon.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Early (proximal) divisions of the sciatic nerve into its tibial and common peroneal components can predispose patients to piriformis syndrome, with these branches passing through and below the piriformis muscle or above and below the muscle. *Acquired * Sitting for prolonged periods (office workers, taxi drivers, bicycle riders) * Overuse syndromes: Piriformis muscle hypertrophy (viz., in athletes) * Trauma to the hip or buttock area
Pathophysiology
When the piriformis muscle shortens or spasms due to trauma or overuse, it can compress or strangle the sciatic nerve beneath the muscle. Generally, conditions of this type are referred to as nerve entrapment or asentrapment neuropathies
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by direct pressure on a nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to nerve root compress ...
; the particular condition known as ''piriformis syndrome'' refers to sciatica symptoms not originating from spinal roots and/or spinal disc compression, but involving the overlying piriformis muscle.
In 17% of an assumed normal population the sciatic nerve passes through the piriformis muscle, rather than underneath it; however, in patients undergoing surgery for suspected piriformis syndrome such an anomaly was found only 16.2% of the time leading to doubt about the importance of the anomaly as a factor in piriformis syndrome. Some researchers discount the importance of this relationship in the etiology
Etiology (pronounced ; alternatively: aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek (''aitiología'') "giving a reason for" (, ''aitía'', "cause"); and ('' -logía''). More completely, e ...
of the syndrome.
MRI findings have shown that both hypertrophy (unusual largeness) and atrophy (unusual smallness) of the piriformis muscle correlate with the supposed condition.
Piriformis syndrome may also be associated with direct trauma to the piriformis muscle, such as in a fall or from a knife wound
A stab wound is a specific form of penetrating trauma to the skin that results from a knife or a similar pointed object. While stab wounds are typically known to be caused by knives, they can also occur from a variety of implements, including bro ...
.
Diagnosis
Piriformis syndrome occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed or pinched by thepiriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.
The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inse ...
of the hip. It usually only affects one hip at a given time, though both hips may produce piriformis syndrome at some point in the patient's lifetime, and having had it once greatly increases the chance that it will recur in one hip or the other at some future point unless action is taken to prevent it. Indications include sciatica (radiating pain in the buttock, posterior thigh, and lower leg) and the physical exam finding of tenderness in the area of the sciatic notch. If the piriformis muscle can be located beneath the other gluteal muscles, it will feel noticeably cord-like and will be painful to compress or massage. The pain is exacerbated with any activity that causes flexion of the hip including lifting, prolonged sitting, or walking.
The diagnosis is largely clinical and is one of exclusion
Exclusion may refer to:
Legal or regulatory
* Exclusion zone, a geographic area in which some sanctioning authority prohibits specific activities
* Exclusion Crisis and Exclusion Bill, a 17th-century attempt to ensure a Protestant succession in En ...
. During a physical examination, attempts may be made to stretch the irritated piriformis and provoke sciatic nerve compression, such as the Freiberg test
Freiberg is a university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called ''Große Kreisstadt'' (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsen district.
Its historic town centre has been placed under heritage ...
, the Pace test
Pace or paces may refer to:
Business
*Pace (transit), a bus operator in the suburbs of Chicago, US
*Pace Airlines, an American charter airline
*Pace Foods, a maker of a popular brand of salsa sold in North America, owned by Campbell Soup Company ...
, the FABER test
Patrick's test or FABER test is performed to evaluate pathology of the hip joint or the sacroiliac joint.
The test is performed by having the tested leg flexed and the thigh abducted and externally rotated. If pain is elicited on the ipsilate ...
(flexion, abduction, external rotation), and the FAIR test
A fair (archaic: faire or fayre) is a gathering of people for a variety of entertainment or commercial activities. Fairs are typically temporary with scheduled times lasting from an afternoon to several weeks.
Types
Variations of fairs incl ...
(flexion, adduction, internal rotation). Sciatica secondary to conditions to be ruled out include herniated nucleus pulposus
Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physic ...
(HNP), facet arthropathy
Facets () are flat faces on geometric shapes. The organization of naturally occurring facets was key to early developments in crystallography, since they reflect the underlying symmetry of the crystal structure. Gemstones commonly have facets c ...
, spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in on ...
, and lumbar muscle strain. Pathology in the sacroiliac joint region, Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
The term sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion, that causes pain in this region.
Signs and symptoms
Common symptoms include lower back pain, buttocks pain, sci ...
and Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis is inflammation within the sacroiliac joint. It is a feature of spondyloarthropathies, such as axial spondyloarthritis (including ankylosing spondylitis), psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis or arthritis related to inflammatory bo ...
are other conditions that present with pain in the low back and hip regions, which may radiate down along the back of the thigh, rarely going down below knee.
Wallet neuritis is an extra-spinal tunnel neuropathy of sciatic nerve, occurring mostly in men. Sitting down on a thick Wallet in the back pocket produces uneven pressure in the hip region that impinges on the Piriformis muscle and / or sciatic nerve. Wallet induced chronic sciatic nerve constriction produces gluteal and ipsilateral lower extremity pain, tingling, and burning sensation.
Diagnostic modalities such as ultrasound Imaging
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal ...
, MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
, CT scan, and EMG are mostly useful in excluding other conditions. Increased thickness Thand increased cross‐sectional area CSA
CSA may refer to:
Arts and media
* Canadian Screen Awards, annual awards given by the Academy of Canadian Cinema & Television
* Commission on Superhuman Activities, a fictional American government agency in Marvel Comics
* Crime Syndicate of Amer ...
for piriformis muscle may be demonstrated on ultrasound imaging and MRI.
Magnetic resonance neurography
Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) is the direct imaging of nerves in the body by optimizing selectivity for unique MRI water properties of nerves. It is a modification of magnetic resonance imaging. This technique yields a detailed image of a ne ...
is a medical imaging technique that can show the presence of irritation of the sciatic nerve at the level of the sciatic notch where the nerve passes under the piriformis muscle. However, Magnetic resonance neurography is considered "investigational/not medically necessary" by some insurance companies. Neurography can determine whether or not a patient has a split sciatic nerve or a split piriformis muscle – this may be important in getting a good result from injections or surgery. Image guided injections carried out in an open MRI scanner, or other 3D image guidance can accurately relax the piriformis muscle to test the diagnosis. Other injection methods such as blind injection, fluoroscopic guided injection, ultrasound, or EMG guidance can work but are not as reliable and have other drawbacks.
Prevention
The most common etiology of piriformis syndrome is that resulting from a specific previous injury due totrauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
. Large injuries include trauma to the buttocks while "micro traumas" result from small repeated bouts of stress on the piriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.
The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inse ...
itself. To the extent that piriformis syndrome is the result of some type of trauma and not neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
, such secondary causes are considered preventable, especially those occurring in daily activities: according to this theory, periods of prolonged sitting, especially on hard surfaces, produce minor stress that can be relieved with bouts of standing. An individual's environment, including lifestyle factors and physical activity, determine susceptibility to trauma of any given type. Although empirical research findings on the subject have never been published, many believe that taking sensible precautions during high-impact sports and when working in physically demanding conditions may decrease the risk of experiencing piriformis syndrome, either by forestalling injury to the muscle itself or injury to the nerve root that causes it to spasm. In this vein, proper safety and padded equipment should be worn for protection during any type of regular, firm contact (i.e., American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team with ...
, etc.). In the workplace, individuals are encouraged to make regular assessments of their surroundings and attempt to recognize those things in one's routine that might produce micro or macro traumas. No research has substantiated the effectiveness of any such routine, however, and participation in one may do nothing but heighten an individual's sense of worry over physical minutiae while have no effect in reducing the likeliness of experiencing or re-experiencing piriformis syndrome.
Other suggestions from some researchers and physical therapists have included prevention strategies include warming up before physical activity, practicing correct exercise form, stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling ...
, and doing strength training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training te ...
, though these are often suggested for helping treat or prevent any physical injury and are not piriformis-specific in their approach As with any type of exercise, it is thought that warmups will decrease the risk of injury during flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ...
or rotation of the hip. Stretching increases range of motion, while strengthening hip adductor
The adductor muscles of the hip are a group of muscles mostly used for bringing the thighs together (called adduction).
Structure
The adductor group is made up of:
*Adductor brevis
* Adductor longus
*Adductor magnus
* Adductor minimus This is ...
s and abductors theoretically allows the piriformis to tolerate trauma more readily.

Treatment
Immediate though temporary relief of piriformis syndrome can usually be brought about by injection of a local anaesthetic into the piriformis muscle. Symptomatic relief of muscle and nerve pain can also sometimes be obtained bynonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
and/or muscle relaxants, though the use of such medication or even more powerful prescription medication for relief of sciatica is often assessed by patients to be largely ineffective at relieving pain. Conservative treatment usually begins with stretching exercises, myofascial release
Myofascial release (MFR, self-myofascial release) is an alternative medicine therapy claimed to be useful for treating skeletal muscle immobility and pain by relaxing contracted muscles, improving blood and lymphatic circulation, and stimulati ...
, massage, and avoidance of contributory activities such as running, bicycling, rowing, heavy lifting, etc. Some clinicians recommend formal physical therapy, including soft tissue mobilization, hip joint mobilization, teaching stretching techniques, and strengthening of the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and biceps femoris to reduce strain on the piriformis. More advanced physical therapy treatment can include pelvic-trochanter isometric stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling ...
, hip abductor, external rotator and extensor strengthening exercises, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS or TNS) is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents ...
(TENS), and massage physiotherapy of the piriformis muscle region. One study of 14 people with what appeared to be piriformis syndrome indicated that rehabilitation programs that included physical therapy, low doses of muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeu ...
s and pain relief medication were effective at alleviating most muscle and nerve pain caused by what the research subjects had been told was piriformis syndrome. However, as this study included very few individuals and did not have a control group
In the design of experiments, hypotheses are applied to experimental units in a treatment group.
In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one tr ...
not receiving treatment (both serious methodological flaws), it provides no insight as to whether the pain in the piriformis would have simply dissipated on its own without any treatment at all, and is therefore not only uninformative, it may actually be misleading. The injury is considered largely self-limiting and spontaneous recovery is usually on the order of a few days or a week to six weeks or longer if left untreated.
Stretching
Most practitioners agree that spasm, strain, or pain in any muscle can often be treated by regular stretching exercise of that muscle, no matter the cause of the pain. Stretching is recommended every two to three waking hours. Anterior and posterior movement of the hip joint capsule may help optimize the patient's stretching capacity. The muscle can be manually stretched by applying pressure perpendicular to the long axis of the muscle and parallel to the surface of the buttocks until the muscle is relaxed. Another stretching exercise is to lie on the side opposite of the pain with the hip and knee of the upper leg flexed and adducted towards the ground while the torso is rotated so that the back of the upper shoulder touches the ground. Physical Therapists may suggest stretching exercises that will target the piriformis, but may also include thehamstring
In human anatomy, a hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in between the hip and the knee (from medial to lateral: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris). The hamstrings are susceptible to injury.
In quadrupeds, ...
s and hip muscles
In human anatomy, the muscles of the hip joint are those muscles that cause movement in the hip. Most modern anatomists define 17 of these muscles, although some additional muscles may sometimes be considered. These are often divided into four g ...
in order to adequately reduce pain and increase range of motion
Range of motion (or ROM), is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another. It is also called range of travel (or ROT), particularly when talking about mechanical devices and in mechanic ...
. Patients with piriformis syndrome may also find relief from applications of ice which will help reduce inflammation and so may help limit pressure on the sciatic nerve. This treatment can be helpful when pain starts or immediately after an activity that is likely to cause pain. As the length of time progresses, heat may provide temporary relief from many types of muscle pain and will temporarily increase muscle flexibility.
Local injections
Failure of conservative treatments such as stretching and strengthening of the piriformis muscle or a high level of immediate pain intensity may bring into consideration various therapeutic injections such as local anesthetics (e.g.,lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidoca ...
), anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
drugs and/or corticosteroids, botulinum toxin (BTX, Botox), or a combination of the three, all of which have a well-documented effectiveness at relieving muscle-related pain. Injection technique is a significant issue since the piriformis is a very deep-seated muscle. A radiologist may assist in this clinical setting by injecting a small dose of medication containing a paralysing agent such as botulinum toxin under high-frequency ultrasound or CT control. This inactivates the piriformis muscle for 3 to 6 months, without resulting in leg weakness or impaired activity. Though the piriformis muscle becomes inactivated, the surrounding muscles quickly take over its role without any noticeable change in strength or gait. Such treatments may be more or less curative (with no return to pain), or may have limited timespans of effectiveness.
Surgery
For rare cases with unrelenting chronic pain, surgery may be recommended. Surgical release of the piriformis muscle is often effective. Minimal access surgery using newly reported techniques has also proven successful in a large-scale formal outcome published in 2005. As with injections, the deactivated/ excised muscle's role in leg movement is completely compensated for by surrounding hip muscles. Failure of piriformis syndrome treatment may be secondary to an underlyinginternal obturator muscle
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen.
The ...
injury.
Epidemiology
 Piriformis syndrome (PS) data is often confused with other conditions due to differences in definitions, survey methods and whether or not occupational groups or general population are surveyed. This causes a lack of group harmony about the diagnosis and treatment of PS, affecting its
Piriformis syndrome (PS) data is often confused with other conditions due to differences in definitions, survey methods and whether or not occupational groups or general population are surveyed. This causes a lack of group harmony about the diagnosis and treatment of PS, affecting its epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
. In a study, 0.33% of 1293 patients with low back pain
Low back pain (LBP) or lumbago is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feel ...
cited an incident for PS. A separate study showed 6% of 750 patients with the same incidence. About 6–8% of low back pain occurrences were attributed to PS, though other reports concluded about 5–36%. In a survey conducted on the general population, 12.2–27% included a lifetime occurrence of PS, while 2.2–19.5% showed an annual occurrence. However further studies show that the proportion of the sciatica, in terms of PS, is about 0.1% in orthopaedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
practice. This is more common in women with a ratio of 3 to 1 and most likely due to the wider quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
femoris muscle angle in the os coxae. Between the years of 1991–1994, PS was found to be 75% prevalent in New York, Connecticut, New Jersey, Pennsylvania; 20% in other American urban centers; and 5% in North and South America, Europe, Asia, Africa and Australia. The common ages of occurrence happen between thirty and forty, and are scarcely found in patients younger than twenty; this has been known to affect all lifestyles.
Piriformis syndrome is often left undiagnosed and mistaken with other pains due to similar symptoms with back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area ...
, quadriceps pain, lower leg pain, and buttock pain. These symptoms include tenderness, tingling and numbness initiating in low back and buttock area and then radiating down to the thigh and to the leg.
A precise test for piriformis syndrome has not yet been developed and thus hard to diagnose this pain.
The pain is often initiated by sitting and walking for a longer period.
In 2012, 17.2% of low back pain patients developed piriformis syndrome.
Piriformis syndrome does not occur in children, and is mostly seen in women of age between thirty and forty. This is due to hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
changes throughout their life, especially during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, where muscles around the pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, including piriformis muscles, tense up to stabilize the area for birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
.
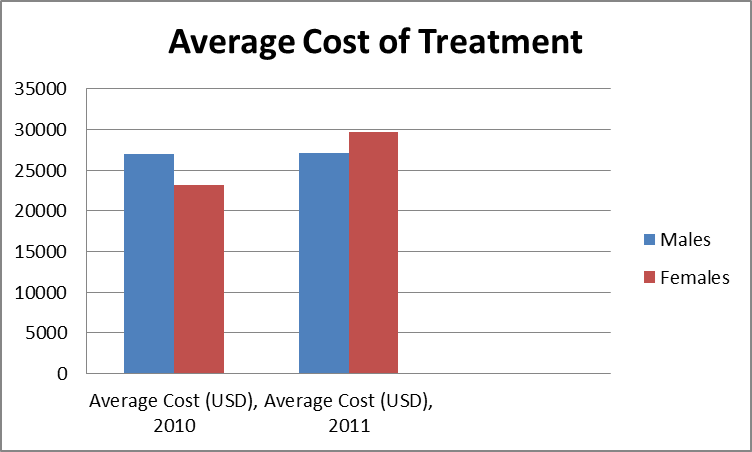
In 2011, out of 263 patients between the ages of 45 to 84 treated for piriformis syndrome, 53.3% were female. Females are two times more likely to develop piriformis syndrome than males. Moreover, females had longer stay in hospital during 2011 due to high prevalence of the pain in females. The average cost of treatment was $29,070 for hospitalizing average 4 days.
References
Further reading
*External links
{{PNS diseases of the nervous system Musculoskeletal disorders Peripheral nervous system disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Syndromes